The main differences between selective wave soldering and wave soldering in PCB processing
Selective wave soldering and wave soldering are both electronic component soldering technologies. The difference lies in the shape of the wave peak and the way the soldering process is controlled. The main difference between wave soldering and selective wave soldering lies in the welding process, applicable scenarios and equipment characteristics.
Wave soldering is a traditional soldering method suitable for mass production of circuit boards with low quality requirements. It immerses the entire circuit board in molten tin and relies on the surface tension of the solder to naturally rise to complete soldering. This method has simple equipment and is suitable for a large number of electronic component production lines.
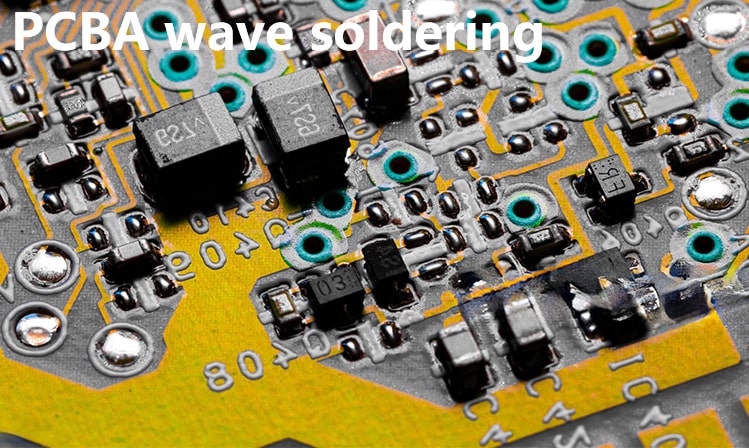
Selective wave soldering is a more advanced welding technology suitable for welding high-precision boards. It sprays dynamic tin waves through the nozzle to accurately weld each solder joint, which can significantly improve the welding quality. Selective wave soldering equipment occupies a small area, saves the use of flux and nitrogen, and is more environmentally friendly.
Selective wave soldering uses gentle wave peaks to control the welding quality by controlling the temperature and angle of the welding head, the area and time of the welding area, and is suitable for connecting electronic components with high reliability requirements.
In terms of applicable scenarios, wave soldering is suitable for mass production of circuit boards with low quality requirements; while selective wave soldering is mainly aimed at high-precision boards and can weld fine components that cannot be processed by wave soldering.
In terms of equipment characteristics, selective wave soldering equipment is more advanced than ordinary wave soldering equipment. Although it is more expensive, it can save the production of flux and tin slag and is more environmentally friendly.
Selective wave soldering and wave soldering are both soldering techniques used to join electronic components. Their main differences lie in the shape of the wave crests and how they are controlled during the welding process. Choosing the appropriate welding technology needs to be determined based on specific needs.







