The difference between SMT patch processing and DIP plug-in processing
With the continuous development of electronic technology, surface mount technology (SMT) and dual in-line plug-in (DIP) plug-in technology have become two common assembly processes in the manufacture of electronic products. Although they are both methods for connecting electronic components, there are obvious differences in process flow, applicable scenarios and characteristics. The main differences between SMT patch processing and DIP plug-in processing are introduced below.
The difference between SMT patch processing and DIP plug-in processing
1. Process flow
SMT patch processing:
SMT patch processing is to directly solder surface mount components (SMD) on the surface of the PCB board, paste the components on the PCB board through welding equipment, and solder them through a hot air furnace or reflow furnace. This process eliminates the pins and holes of the components, making the layout of the PCB board more compact and suitable for the manufacture of high-density circuit boards.
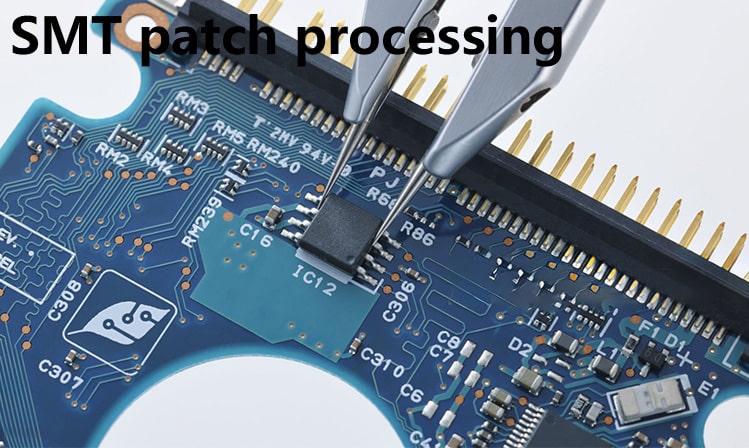
DIP plug-in processing:
DIP plug-in processing is to connect by passing the pins of the plug-in components through the holes on the PCB board and soldering the pins on the other side of the PCB board. This process requires the use of wave soldering or manual soldering to complete the welding work. Compared with SMT patch processing, the process is relatively complex and is suitable for some special scenarios or situations where the PCB board layout requirements are not high.
2. Applicable scenarios
SMT patch processing:
SMT patch processing is suitable for the manufacture of electronic products that require high-density layout, miniaturized design and automated production, such as smart phones, laptops, etc. Since SMT technology can achieve highly automated production, it has obvious advantages in mass production. Mass-produced electronic products, such as consumer electronics
DIP plug-in processing:
DIP plug-in processing is suitable for some electronic products that have low layout requirements, small quantities or large component sizes, and products that require high mechanical strength, such as industrial equipment. There is also prototyping and small-batch production in the R&D stage. In addition, some special components such as high-power resistors, capacitors, etc. are not suitable for SMT patch processing due to their large size, so DIP plug-in processing is more appropriate.
3. Features and advantages
Features and advantages of SMT patch processing:
- The layout is more compact and high-density integration can be achieved.
- High production efficiency, suitable for mass production.
- Suitable for the manufacture of miniaturized design and lightweight products.
- Fast signal transmission speed, short signal transmission distance, and good electrical performance.
Features and advantages of DIP plug-in processing:
- High flexibility, suitable for sample making and small batch production.
- More convenient for processing some special components and large-size components.
- Traditional process, simple process flow, easy operation and maintenance.
- Strong adaptability, insensitive to environmental changes, suitable for various working environments
SMT is suitable for high-density, miniaturized, and large-volume electronic product manufacturing.
DIP is suitable for small-batch production or R&D products that require high mechanical strength and strong environmental adaptability.
Choosing the right processing method according to specific needs can effectively improve production efficiency and product quality.
If you want to know more, you can pay attention to PCBAMake. If you need to know more about PCB proofing, SMT patch, and PCBA processing related technical knowledge, please leave a message for consultation







