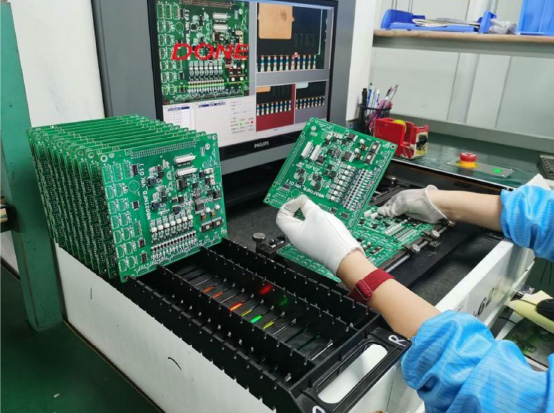
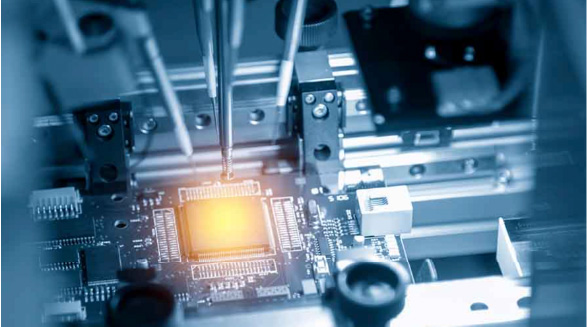
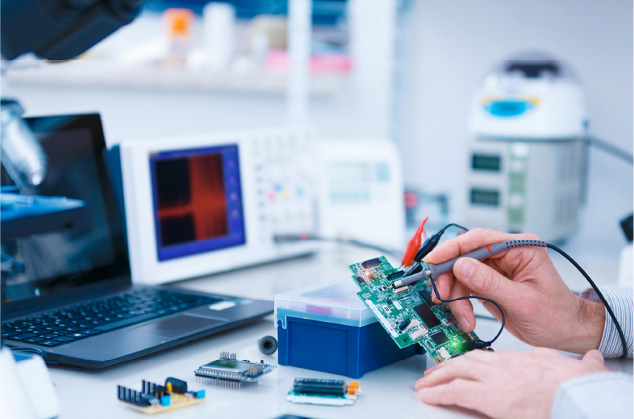
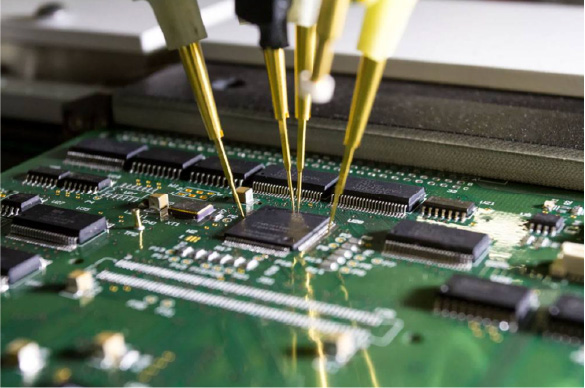
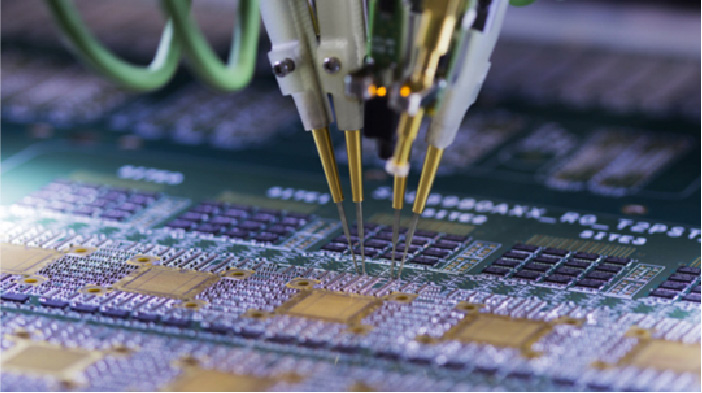
A functional circuit test is exactly what it sounds like — it tests the function of the circuit. This type of testing always comes at the end of the manufacturing plan, using a functional tester to check whether a finished PCB performs to specifications.
Some answers to common questions about functional circuit tests and how they work can be found below:
How do functional testers work? Functional testers come in several types but generally share the same function — they simulate the final environment in which the PCB is supposed to function. Functional testers usually do so by interfacing with the PCB via its test-probe points or edge connectors and testing to certify that the PCB functions according to design specifications.
Are functional circuits the same as ICTs? In some ways, functional circuit tests are similar to ICTs in that they use connectors to attach to the board. In the case of functional circuit testers, they use pogo pin devices to connect to the PCB and generally need fewer pins than an ICT fixture. The test equipment then runs programs to test the PCB, ensuring that the equipment functions exactly as intended.
When do functional circuit tests occur? As previously stated, functional circuit tests are the last type of test to complete in a PCB manufacturing plan, ensuring that the product going out functions according to specifications.
What does a functional circuit test evaluate? Generally, functional circuit tests just look at the product’s functionality as a whole and grade it on a pass or fail basis. As a result, it’s not an ideal testing method for early prototypes since it doesn’t identify details about what’s wrong with the product.